

LONG-TERM SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF LIRAGLUTIDE AFTER BARIATRIC SURGERY IN A REAL-WORLD SETTING IN CHILE
Farías MM¹ | ¹Nuclinic Medical Clinic, Las Condes, Santiago, Chile
OBJECTIVES
To describe the safety and effectiveness (relative change in body weight) among Chilean patients receiving liraglutide after bariatric surgery (BS) in a real-world setting.
INTRODUCTION
- Sustainable weight loss and improvement and/or resolution of metabolic comorbidities are strong benefits of bariatric surgery (BS).¹
- Nevertheless, irrespective of initially successful weight loss, weight regain may occur during long-term follow-up and a relevant proportion of patients fail to reach or maintain their target weight goals.²
- Liraglutide is a therapy aimed to avoid weight regain.3 Liraglutide had no insurance coverage as a treatment for obesity in Chile and all patients pay for their own treatment.
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
Table 1. Main demographic data
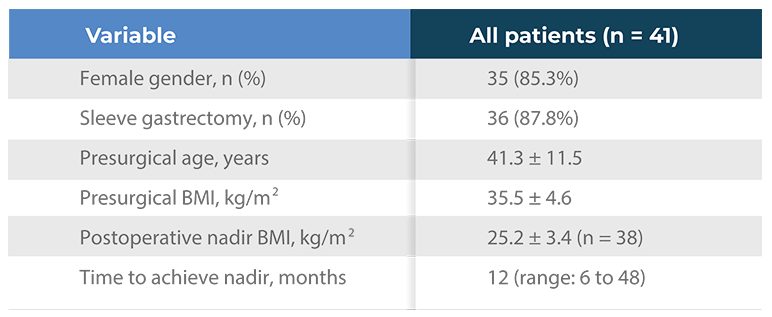

- Dropout rates were consistent with usual treatment practice of people living with obesity
KEY SAFETY RESULTS
- Forty-one participants were included in the study.
- Treatment with liraglutide was well tolerated; no mortality cases or major complications were observed.
- Six mild gastrointestinal adverse events were reported by 5 patients (12.2%; abdominal discomfort, n = 3; reflux, n = 2; constipation, n = 1).
- No gastrointestinal adverse events led to treatment interruption.
- After 12 months of treatment, one patient required cholecystectomy due to cholelithiasis.
Table 2. Liraglutide treatment
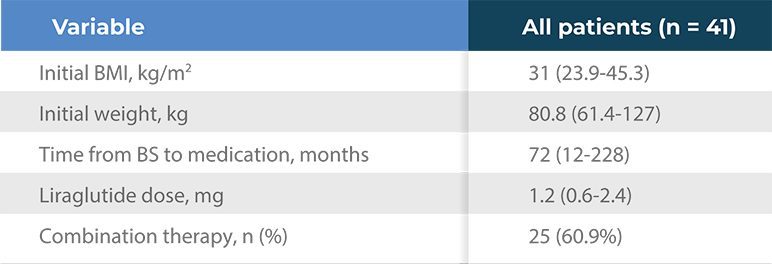

- All values are median (range), excepting when specified
STUDY DESIGN
- Retrospective, observational, single-arm, pre-post study including patients who had initiated liraglutide between 2017 and 2020 from a single obesity physician’s private practice in Santiago, Chile.
- The inclusion criteria were (1) patients who assisted for pharmacological treatment of obesity after a minimum 3-month follow-up period after starting liraglutide treatment following a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or sleeve gastrectomy (SG) at different Chilean medical centers; (2) at least one control visit after liraglutide treatment start.
- Liraglutide dose was defined as the maximum dose that could tolerated and afforded during the follow-up period.
- Clinical perception of hunger sensation, satiation, satiety and emotional eating was considered for increasing liraglutide dose or adding a second drug in subject who did not tolerate increasing doses of liraglutide or could not afford treatment costs.
Figure 1. Mean BMI variation from baseline during follow-up
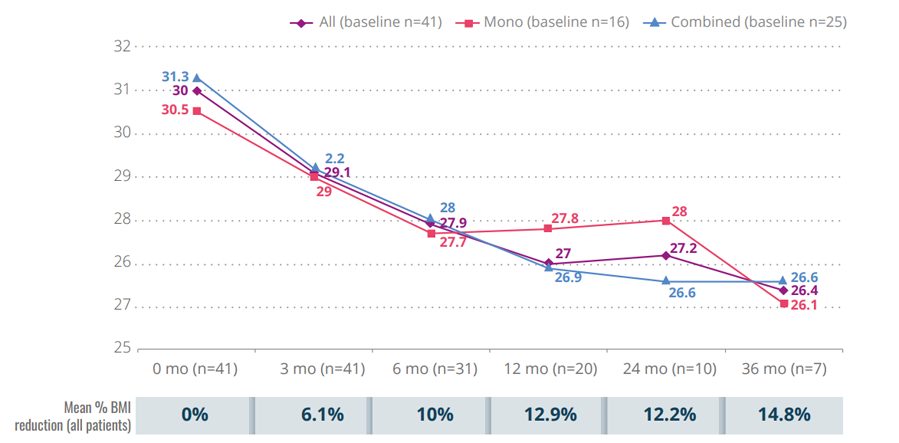

KEY EFFECTIVENESS RESULTS
- Liraglutide administration was associated with mean weight loss rates from baseline at 3, 6, 12, 24, and 36 months of 5%, 7.7%, 7.6%, 5.8%, and 5.1%, respectively.
- Mean body mass index reduction reached 14.8% at 36 months.
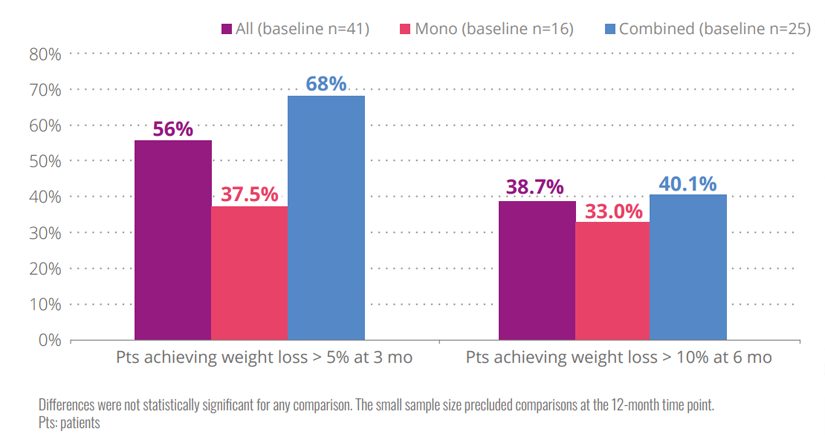
- Results were similar for monotherapy or combined therapy without significant differences at any point.
Figure 2. Patients achieving weight loss according to treatment

CONCLUSION
Liraglutide, as a monotherapy or combined with other pharmacological strategies, is a safe and effective treatment to maintain weight reduction and avoid weight regain in BS patients attending routine clinical care in a Chilean setting.
REFERENCES: 1. Stenberg E, Dos Reis Falcão LF, O’Kane M, et al. Guidelines for Perioperative Care in Bariatric Surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Society Recommendations: A 2021 Update. World J Surg. 2022; 46(4):729-51;
2. Elhag W AW. Weight Regain and Insufficient Weight Loss after Bariatric Surgery: A Call for Action. In: Saiz-Sapena N (ed). Bariatric Surgery – From the Non-Surgical Approach to the Post-Surgery Individual Care [Internet]. London:
IntechOpen; 2020. Available at: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/74559; 3. Alruwaili H, Dehestani B, Le Roux CW. Clinical Impact of Liraglutide as a Treatment of Obesity. Clin Pharmacol Adv Appl. 2021;13:53-60
Conflict of interests as declared by the author: Maria Magdalena Farías has received honoraria as speaker from Novo Nordisk.
Medical writing support was provided by Agencia Médica and funded by Novo Nordis
